INDUCTION HARDENING
Induction Hardening Heat Treatment
Among the heat treatments of steel or cast iron, the induction hardening is particularly relevant, used to increase the surface hardness of mechanical parts particularly subject to wear, whose strength and fatigue limit is greatly improved, significantly extending the life cycle.
Induction hardening is preferable, compared to other heat treatments with oven heating such as eg. nitriding, for
- the efficiency of performance,
- the speed,
- energy saving
In fact, similar mechanical characteristics are obtained through a more convenient treatment in terms of time and costs, with the advantage of having practically no limitations in the shape and size of the pieces to be processed, applicable on single details up to large volumes, associated with considerable energy savings. resulting from the immediate heating (thanks to induction) of specific and limited areas of the part to be treated.
Induction Hardening vs Nitriding
Compared to nitriding, then, induction hardening allows to reach much greater hardening depths and without requiring specifically dedicated types of steel, as it is based on the structural transformation of the material and not consequent to a chemical reaction as occurs, in fact, for nitriding (in this case triggered by the forced absorption of nitrogen).
The speed of the induction hardening process makes it, compared to other mechanical processes, a rather "lean" construction phase: in a few steps, based on the study of the mechanical design and the required requirements, it is possible to formulate an estimate by agreeing on the conditions of supply and delivery times, the latter generally in the order of a few days but, in urgent cases, even of only 1!
In the service we offer as Termostahl, in fact, thanks to the many systems installed and the flexibility of the production organization, it is possible to assign specific priorities and plan the treatment on the first suitably available machinery, facilitating the customer's request as much as possible.
In this regard, for particular situations and mechanical parts that are difficult to transport, taking advantage of the installation / dimensional characteristics of some of our systems, we can perform the hardening treatment also "on site" at the customer's construction site, moving the hardening and necessary equipment.
The know-how acquired, the support for the cost / benefit analysis already in the design phase, accurate feasibility checks and dedicated inspections also allow us this rare but useful feature.
Induction Hardening: Technical Details
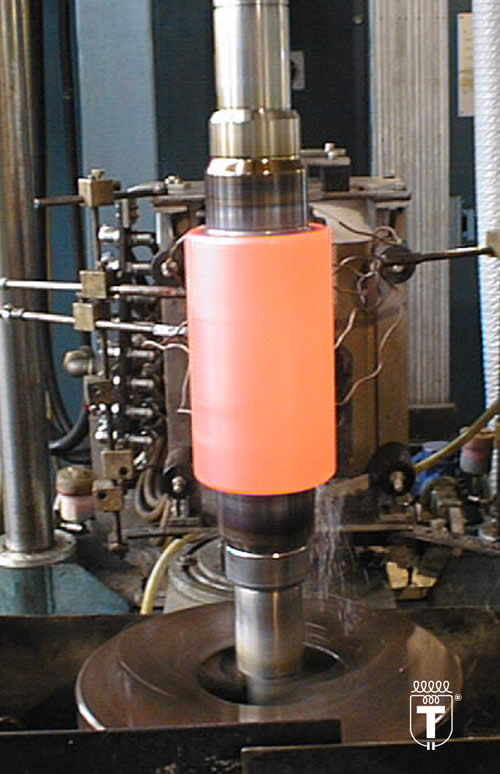
The heat treatment of induction hardening consists in the rapid heating of the area to be reinforced, at a temperature above the austenitization point of the Ac3 steel (900 ° - 950 °), in maintaining it at this temperature for an appropriate homogenization time of the material and in the subsequent rapid cooling (with jets of water or other coolants), in order to achieve the desired transformation.
The temperature at which the steel heats up, and the residence time at this temperature, must allow the starting structure to become completely austenitic without exceeding criticality thresholds. Therefore the cooling speed must be particularly high and controlled, to avoid reaching temperatures which, if otherwise exceeded, could instead trigger unwanted and not advantageous transformations.
In the heat treatment of induction hardening, the production of heat is achieved by currents, as the name suggests, "induced" in the body to be heated when it is subjected to the action of an alternating magnetic field.
The magnetic field is generated by an induction coil which electromagnetically transfers the energy to the body to be heated and therefore without direct contact between the elements.
The induced currents, also called "eddy currents", give rise to losses due to the Joule effect directly in the material to be heated, which constitute the heat sources necessary to increase the temperature of the body.
The magnetic field of excitation is obtained by circulating an alternating current, of suitable intensity and frequency, within an induction coil generally made with a copper tube (internally cooled by water circulation).
By exploiting this characteristic of conducting bodies which, precisely, if crossed by alternating current give rise to a surrounding magnetic field and induced currents in the neighboring conductors, the distribution of which depends on the frequency of the excitation field, acting precisely on the frequency of the current and by varying it according to needs (by means of frequency converters), it is possible to obtain different depths of hardening.
Specifically, HIGH FREQUENCY systems are used, based on currents between 100 - 1000 KhZ, for induction hardening heat treatments such as to obtain medium-low depths of hardening, usually on small mechanical parts.
MEDIUM FREQUENCY induction hardening systems, between 3 - 100 KhZ and with powers from 10 - 1,000 Kw, to obtain greater depths of hardening on medium-large pieces.
For heating at great depths, LOW FREQUENCY induction hardening systems are used, between 50 - 500 hZ.
Induction hardening - Applications
Induction hardening, due to the advantages it offers, is performed on an extensive range of mechanical products, covering different industrial sectors. Here are some examples of application in different sectors.
- Automotive: crankshafts / camshafts, transmission and steering parts, drawing and shearing molds (from which to obtain doors, hoods, panels, etc.), cutting blades, nuts and bolts.
- Railway: multiple components of rolling stock, exchange boxes, various levers.
- Naval: transmission shafts, gears, parts for military applications.
- Oil & Gas: sliding shafts, gear wheels, pinions typically used in off-shore platforms.
- Aeronautical: pins, shafts, various gears.
- Metallurgical: rolling cylinders, work rolls, back-up rolls, toothed crowns, worm screws.
- Various sectors (sheet metal / paper / chain mills / machine tools / food): special bearings, cylinders for leveling machines, spiral rollers, embossed rollers, plates, bushings, cams, headworks, linear guides, wheels for bridge cranes, columns for presses, etc.
As Termostahl we have been operating in the induction hardening field for more than 60 years, in all industrial sectors in which this treatment is applied, particularly with Italian customers in the north-central Italy areas for substantially logistical reasons, as transport costs can significantly affect but, when required, we also work with companies in southern Italy and neighboring European countries such as France, Switzerland and Slovenia.
Our range of action extends from Turin to Udine and up to Bologna-Florence, including all the major manufacturing districts of the provinces of Milan, Brescia, Bergamo, Verona, Vicenza, Padua, Venice, Pordenone, Parma, Modena, Genoa.
We also actively cooperate with Research Centers and University laboratories for the engineering of specific production processes, as many times the requirements defined in the design phase, in order to be applied widely and in complete safety, require particular optimizations and fine-tuning.





